Standards, Tools and Procedures in Accessible eBook Production
Introduction
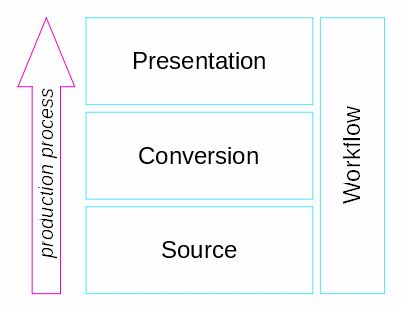
The accessible ebook production process is highly versatile and thus requires many different steps and procedures. In general they can be categorized into the following four classes
- The source document or script where the accessible ebook production process starts from: This can vary from an actual printed book to a file from a common word-processing application or a PDF, up to a file in a Desktop Publishing Tool (DTP), such as InDesign or Quark Xpress.
- The conversions within the production process: Addressing complexity e.g. linear access of non-linear materials (vision) and better readability (cognition). Books may consist of different levels of complexity, beginning from novels to complex structures of workbooks with many graphics, mathematical formulas or scientific symbols for school pupils or students, including also books with multilingual text.
- The Presentation of the content: Different user needs require different presentation modalities of the same content. This may inclued personalised access issues like DAISY, haptic or audio presentation. Not to forget the need of upholding the rights of all stakeholders in the process (authors, publishers, etc.). This may also result in additional requirements in the ebook production and presentation process.
- The production workflow: Can be seen as a transversal class affecting all three of the above mentioned steps. Efficient production of accessible and personalised materials, including standards, legislation, involving publishers and authors, management, user involvement and delivery services.
All the above mentioned needs demand more and intense R&D to make the process of ebook production more efficient, faster and the products better accessible and usable.
Challenges and Call for Contribution
Different formats, type and structure of information (graphics, images, etc.) and the different level of complexity pose a great challenge in the process. Also the delivery to end-users of the ebooks should be targeted in this STS. Since the variance in the target group is very high (print disabled, cognitive disabled, hearing impaired persons) it is also challenging to deliver the right content in the right form to the right target reader. To implement and reference all the different representations of information should be a field of scope in this STS. Also an outlook beyond the current practice into the future of accessible ebook production procedures. This Special Thematic Session is organised to tackle the above issues in an inclusive way. We are considerably interested in research results that deal with challenges as
- Software / Plugins
- Standards and their application
- Production Procedure, Automation of the Process
- Tools
- Work flow
- Formats
- Distribution (Libraries, Meta Data, etc.)
- Speeding up OCR process
- Development of administrative meta data
- Automatic relation between inline elements, side marks
- Accessible Graphics (reuse of graphics sub elements) historical and new standards for haptic graphics or/and audio descriptions / audio tactile combinations
- Cataloguing/referencing system. (Referencing audio description, tactile representation, easy to read version and/or swellcopy versions, etc.
- Service provision and delivery
- Training of involved parties
Contributions to the STS have to be submitted using the standard submission procedures of ICCHP.
This STS and the workshop on Accessible eBook Production is featured by and organised in co-operation with
Chairs

Georgios Kouroupetroglou, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Greece
Reinhard Ruemer, BookAccess
Tomas Murillo Morales, JKU
Klaus Miesenberger, Johannes Kepler University Linz
Contributions to a STS have to be submitted using the standard submission procedures of ICCHP24.
When submitting your contribution please make sure to select the right STS from the drop-down list "Special Thematic Session". Contributions to a STS are evaluated by the Programme Committee of ICCHP-AAATE and by the chair(s) of the STS. Please get in contact with the STS chair(s) for discussing your contribution and potential involvement in the session.